Optical Switch Wavelength Selection Guide: Find the Optimal Wavelength for Your Application
As the core component of optical communication and optical sensing systems, the wavelength selection of optical switches directly affects the performance and efficiency of the system. This article will explore the key factors in optical switch wavelength selection to help you find the best wavelength for your specific application.
1. Understanding Optical Switch Wavelength
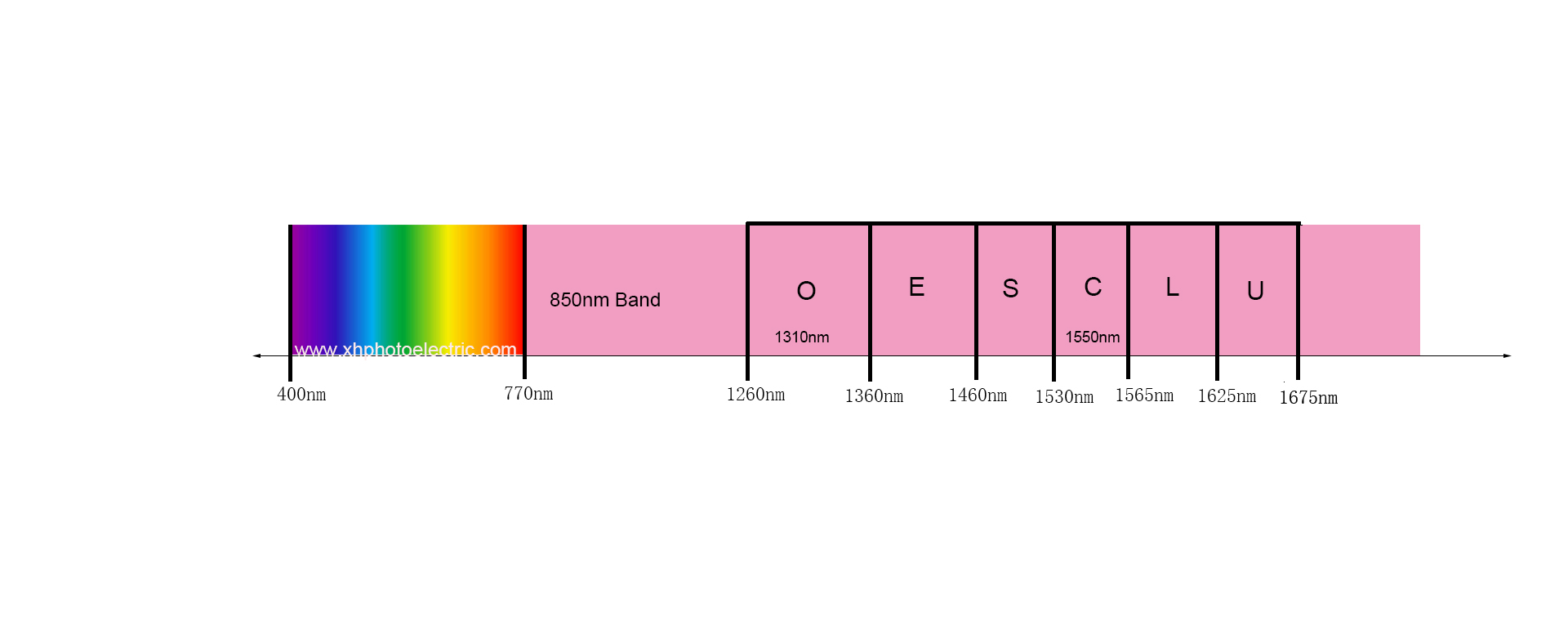
The optical switch wavelength refers to the range of light wavelengths that the optical switch can effectively operate, usually in nanometers (nm). Common optical switch wavelength ranges include:
850 nm: multimode fiber communication
1310 nm: single-mode fiber communication, low loss window
1550 nm: single-mode fiber communication, minimum loss window
2. Key Factors Affecting Wavelength Selection
When selecting an optical switch wavelength, the following key factors need to be considered:
Application scenario: Different application scenarios have different requirements for wavelength. For example, optical fiber communication usually uses 1310 nm or 1550 nm, while optical sensing may require a specific wavelength to match the absorption characteristics of the substance being measured.
Light source: The optical switch needs to match the wavelength of the light source. For example, if you use a 1550 nm laser, you need to choose an optical switch that supports the 1550 nm wavelength.
Fiber Type: Different types of optical fibers attenuate optical signals at different wavelengths differently. For example, multimode fiber is suitable for 850 nm, while single-mode fiber is suitable for 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
Optical Switch Type: Different types of optical switches have different sensitivity to wavelength. For example, MEMS optical switches usually have a wide wavelength range, while waveguide-based optical switches may be more sensitive to wavelength.
Cost: Optical switches for different wavelengths may have different costs. For example, a 1550 nm optical switch is usually more expensive than a 1310 nm optical switch.
3. Wavelength selection for common application scenarios
Fiber optic communication:
Short distance, multimode: 850 nm
Long distance, single mode: 1310 nm or 1550 nm
Optical sensing:
Gas sensing: Select the wavelength corresponding to the absorption peak of the gas being measured
Biosensing: Select the wavelength corresponding to the absorption or fluorescence characteristics of biomolecules
LiDAR:
1550 nm: Eye-safe, high atmospheric transmittance
4. Other considerations
Wavelength range: The wavelength range of the selected optical switch should cover all the wavelengths you need.
Insertion loss: Select an optical switch with low insertion loss at the target wavelength.
Crosstalk: Select an optical switch with low crosstalk at the target wavelength.
Reliability: Select an optical switch with high reliability at the target wavelength.
Optical switch wavelength selection is a complex process that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. By understanding the concept of optical switch wavelength, the influencing factors, and the wavelength selection for common application scenarios, you can find the best wavelength for your application to optimize system performance and efficiency.
It is recommended that you consult our professional engineers when selecting the wavelength of the optical switch to obtain more professional advice and technical support.
Comments are closed